What are Hepatitis C genotypes?
Hepatitis C is split into six unique genotypes all over the world these genotypes have along with several subtypes. However, it is labelled into 1 to 6 types. In these days many people are infected with genotype 1.
People are infected by anyone genotype, each contains the combination of their relevant viruses which known as quasi-species. There is alternative medical treatment avail for hepatitis c virus.
Different genotypes react differently so it is very important to know about Hepatitis C genotype before treatment. For this, testing will be processed with a blood test. Doctor offer drug treatment based on the type of HCV genotype infected on your body.
To cure HCV different treatment is undertaken for a specific person. Genotype is consisting of nucleic acid which presents on the DNA molecule. Exclusive techniques are used for different phenotypes. It is various forms or alleles. On the treatment, doctors understand current immune and process treatment faster.
Why are genotypes important for treatment?
Knowing your HCV genotype is important information that can help patients and doctors find the most effective treatment.
Understanding of HCV genotype is very important; it is the initial part of a treatment that can help doctors to find out most recommended effective treatment for their patients. It helps to determine patient’s hormones, which medicines are chosen, and how long treatment should be.
Almost all the Hep C genotypes can create a serious liver problem. However, in certain cases, most of the peoples who are infected with HCV Hepatitis C genotype 1, have the higher chance of developing cirrhosis. Generally, Hep C genotype 1 and 3 can cause the risk of liver cancer.
All oral and direct acting antivirals (DAAs) are capable enough to prevent the occurrence of Hep C virus. Today, it is mostly cured by direct-acting antivirals, medication to protect HCV easily. It allows detecting virus on the immune system and boosting your body with essential proteins. Direct acting antiviral block steps in the life cycle of virus and cure all level of genotype with the constant rate.
Genotype Table: Recommended Treatments for Hepatitis C Genotypes 1, 2, 3,4,5,6.
| Generic Brand Name | Formulation | Approved Genotypes | Usual Instructions | Major Side Effects | Manufacturer Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velpanat, Velasof, MyHep All, Sovihep V, Resof Total | 100/400 mg Sofosbuvir+Velpatasvir | Hepatitis c Genotype 1,2,3,4,5,6 all types treatment | A pill taken once a day for 12 weeks. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy |
| Hepcinat LP, Ledifos, Myhep LVIR, Ledihep, Resof L | 400/90 mg Sofosbuvir+Ledipasvir | Hepatitis c Genotype 1, 4, 5, 6 treatment. It is mainly used to treat Hep C | A combination pill taken once a day. It’s usually taken for 12-24 weeks, and sometimes only 8 weeks. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy |
| Hepcinat, Sofovir, Myhep, Sovihep, Resof | 400 mg Sofosbuvir | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | 1 Sofosbuvir pill and 1 Daclatasvir pill once a day for 12 weeks. Sometimes used with Ribavirin. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy |
Different Types of HCV genotypes:
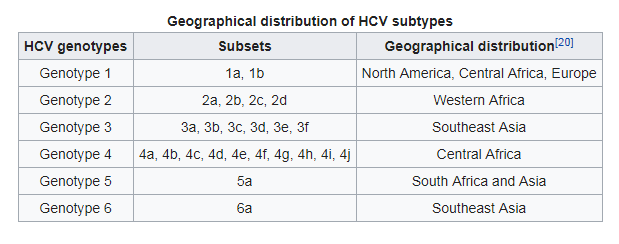
There are generally six main kinds of genotypes of hepatitis C virus genotype 1, 2,3,4,5 and 6. These include many subtypes.
Underdeveloped countries are mostly affected by Genotype 4 and 5. Genotype 4 is most commonly found in the Middle East and Africa.
United States is mostly affected by Hepatitis C genotype 1.
Hepatitis C Genotypes 1,2 and 3 are found throughout the world.
Genotype 5 is common in South Africa.
Asians are mostly affected by Genotype 6.
Genotype 1
North America and Europe are mostly affected by Hep C Genotype 1. It affects for more than 80% cases in the US. Infections caused by this genotype are most difficult to treat. But new developing direct-acting antivirals are successful in treating new and previously affected individuals. It can further be divided into subtype 1a, 1b and 1c.
Genotype 2
Genotype 2 accounts for almost 10% of the cases. It is the second most common type in the US. Previously, it was the most easily treated Hepatitis with patients about 80% chance of cure and attaining a sustained viral response(SVR). Now after the introduction of DAAs chances of cure are 90% in old patients and up to 99% in new patients.
Genotype 2 has subtypes 2a, 2b and 2c.
Genotype 3
Genotype 3 is most common in South East Asia and roughly spread across Australia, India and some parts of Far East. About 6% of Americans have the gene of this genotype. It has two subtypes 3a and 3b.
Genotype 4:
Africa, Middle East, and several Eastern Europe countries are the breeding grounds for this genotype. Egypt which has the most number of patients with HCV also has the most numbers of Genotype 4 sufferers. They have subtypes 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d and 4e.
About 90% of Genotype 4 sufferers are found in the Middle East and Africa.
Genotype 5:
It has only one subtype 5a and is most commonly seen in South Africa.
Genotype 6:
It also has only subtype 6a. It is most common in southern China, Hong Kong and Southeast Asian countries.
Which genotype is difficult to treat?
In these days, genotype 3 is very hard to treat. Hep C genotype 3 is most commonly found in South Asia, Southeast Asia and Northern Europe. It leads to the deterioration of conditions like liver diseases, steatosis which is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma or cancer. Genotype 3 also creates resistance to insulin and makes the liver break down fats. This makes it harder to treat. However new Hep C treatment Sofosbuvir+Velpatasvir is available to treat genotype 3.
What tests are required to know the genotype of Hep C virus?
If a patient has been diagnosed with HCV, the doctor runs Hepatitis C test for viral load and genotype. The best treatment can only be decided after knowing the genotype.
Genotype tests can be run on blood taken from fingersticks or blood draws. Tests should be run again to determine if the patient is cured or the infection is chronic.
Medications are prescribed based on the availability in the area and payer.